Test design
Experimental animals: Female clean-type Kunming mice weighing (19±2) g were selected as research subjects. After purchase, they were adaptively fed for 3 days before being used in experimental research.
Effects of xylo-oligosaccharides on blood sugar levels and alanine aminotransferase activity in diabetic mice: After fasting for 24 hours, the mice were given a one-time intraperitoneal injection of 5% tetroximidine (dose: 200 mg/kg), and then at 72 After one hour, the eyeballs were removed to collect blood, the serum was separated, fasting blood glucose was measured, and mice with blood glucose levels 100% higher than the normal value were selected as diabetic mouse models. Normal control group A: Normal mice were given 0.2 ml of normal saline once a day; Normal mice were given xylo-oligosaccharide group B: Normal mice were given 0.2 ml of xylo-oligosaccharide aqueous solution once a day, the dose was 350 mg/(kg ·d); Diabetic control group C: Diabetic mice were gavaged with 0.2 ml of normal saline once a day; Diabetic mice given xylo-oligosaccharide group D: Diabetic mice were gavaged with 0.2 ml of xylo-oligosaccharide aqueous solution once a day, the dose was 350 mg/(kg·d); Diabetic mice given acarbose group E: Diabetic mice were orally administered 0.2 ml acarbose aqueous solution once every morning and evening, with a dose of 20 mg/(kg·d); during the experiment, mice Free access to food and water. Body weight was measured daily, and 14 days later, the eyeballs were removed and blood was collected to measure fasting blood glucose and serum ALT activity.
Effect of xylo-oligosaccharides on blood lipid content in hyperlipidemic mice: The high-fat solution is: 20% triolein, 10% cholesterol, 5% porcine bile salts, 65% water, stir with hot distilled water to form a suspension liquid. Normal control group A: mice were given 0.2 ml of normal saline once a day; hyperlipidemia control group B: mice were given 0.2 ml of high-fat solution once a day; hyperlipidemia group C: Xylo-oligosaccharide was added to the lipid solution so that the dose of the latter reached 350 mg/(kg·d), and 0.2 ml was administered to the mice daily. During the experiment, the mice had free access to food and water. After 28 days, the eyeballs were removed and blood was collected to measure the levels of TG, TC and HDL-C in the serum.
test results
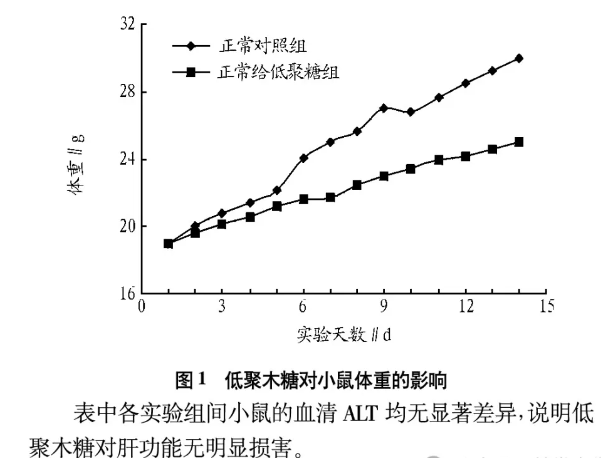
(1) Effect of xylo-oligosaccharides on body weight of normal mice
As can be seen from Figure 1, the weight of normal control mice increased significantly during the experimental period, while the weight gain of mice administered xylo-oligosaccharide was slower and smaller, indicating that xylo-oligosaccharide has the effect of inhibiting the weight growth of mice.
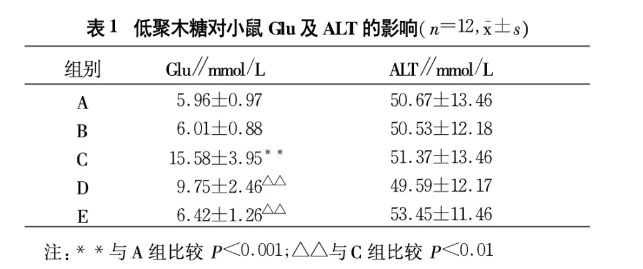
(2) Effects of xylo-oligosaccharides on Glu and ALT in diabetic mice
As can be seen from Table 1, the Glu value of mice in the diabetic control group is significantly different from that of the normal control group (P<0.001), indicating that the experimental hyperglycemic animal model was successfully established and can be used reliably for hypoglycemic research. After 14 days of oral administration of xylo-oligosaccharide to diabetic mice, test results showed that it could reduce the Glu level of the mice (P<0.01) and had a significant therapeutic effect on hyperglycemia. At the same time, it can be seen that although xylo-oligosaccharide can significantly reduce hyperglycemia in diabetic mice, it has no significant effect on blood sugar in normal mice. There was no significant difference in serum ALT of mice between each experimental group, indicating that xylo-oligosaccharides did not significantly damage liver function.
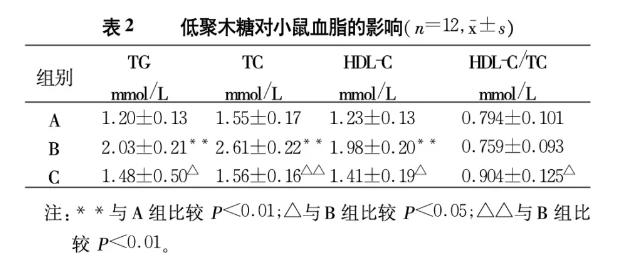
As can be seen from Table 2, the mice in the hyperlipidemia control group had reduced appetite, and their coat color was dark and untidy in the later period. The contents of TG, TC, and HDL-C in the serum were significantly different from those in the normal control group (P<0.01), suggesting that the use of The mouse model of hyperlipidemia was successfully established by intragastric administration of high-fat solution. After administrating xylo-oligosaccharide to hyperlipidemia mice for 28 days, the TC content decreased significantly (P<0.01), and the TG and HDL-C contents decreased (P<0.05), indicating that this xylo-oligosaccharide can reduce the experimental These three serological indicators in mice play a role in lowering blood lipids. At the end of the test, the HDL-C/TC ratio of the mice in the hyperlipidemia group given xylo-oligosaccharide was greater than that in the hyperlipidemia control group (P<0.05), indicating that xylo-oligosaccharide does have a certain effect against experimental hyperlipidemia in mice. forming effect.
Test Conclusions
In order to study the effects of xylo-oligosaccharide on blood sugar and blood lipids in mice, a diabetic mouse model was constructed using alloximidine, and a mouse model of hyperlipidemia was established by feeding a high-fat solution. Rat body weight, serum blood glucose (Glu), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) contents showed that oligomeric wood Sugar can reduce the weight of normal mice, effectively reduce the Glu content of diabetic mice without changing ALT, reduce the levels of TG and TC in hyperlipidemia mice, and increase the ratio of HDL-C to TC, indicating that taking oligomeric wood Sugar plays a certain role in preventing and treating hyperlipidemia, arteriosclerosis and coronary heart disease.














